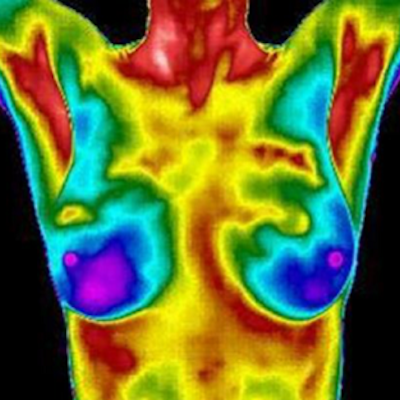
Comparison of Breast Screenings
Home » Good Breast Health » Comparison of Breast Screenings
MAMMOGRAPHY
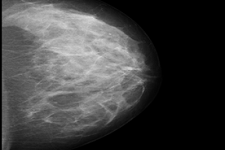
After breasts are compressed between two firm surfaces to spread out the breast tissue, an X-ray captures black-and-white images that are displayed on a computer screen and examined by a radiologist. A Mammogram is the only test that can detect and monitor micro calcifications. Mammography can detect a lump or mass after it reaches 1 centimeter in size. This screening exposes breasts to radiation and is not effective for screening women with dense breasts.
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
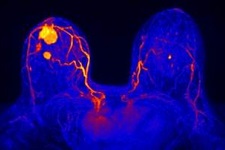
Magnetic Resonance Imaging, also known as an MRI, uses magnets and radio waves instead of x-rays to produce very detailed, cross-sectional pictures of the breasts. For breast MRI to look for a lump or mass, a contrast liquid (called gadolinium) is injected into a vein before or during the scan to show details better. This screening is more expensive than a Mammogram or Ultrasound and is effective for women with dense breasts.
ULTRASOUND
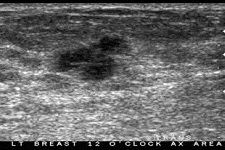
Ultrasound imaging of the breast uses sound waves to produce pictures of the internal structures of the breast. It is primarily used to help diagnose breast lumps or other abnormalities your doctor may have found during a physical exam, mammogram or breast MRI. The primary use of breast ultrasound is to help diagnose breast abnormalities detected by a physician during a physical exam (such as a lump) and to characterize potential abnormalities seen on mammography or breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Ultrasound imaging can help to determine if an abnormality is solid (which may be a non-cancerous lump of tissue or a cancerous tumor), fluid-filled (such as a benign cyst) or both cystic and solid. Ultrasound is safe, noninvasive and does not use radiation.
HOW TO PREPARE FOR
YOUR THERMOGRAM
QUICKLINKS
TESTIMONIALS
Gaye Walden is a true gem for women like me who want to learn more about breast health and overall wellness. She has tremendous passion for breast health and provided me with a wealth of information and resources to help me in my journey. She is so generous in her sharing and I am very grateful for the time she spent with me as well as her expertise.
Being Proactive
I can not say enough about my experience with Gaye Walden, not only was she qualified and her expertise exemplary, but her demeanor and patience put me in a feel good mood leaving me less worried. I hope more women take the initiative to put their health in perspective with a Thermogram which will better serve their needs now and in the future.
- Nancy